Tomato Yellow Leaf Curl Virus (TYLCV): Physiology, Management Practices, and Control Measures in the Context of Nepal
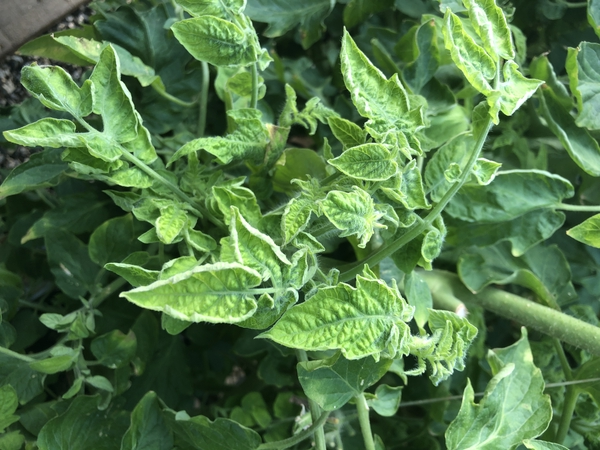

Tomato Yellow Leaf Curl Virus (TYLCV) is a devastating plant pathogen causing significant economic losses in tomato production worldwide, including in Nepal. The virus belongs to the genus Begomovirus within the family Geminiviridae. It primarily affects solanaceous crops, with tomatoes…